
Dr. Wei Deng, Associate Professor
Tel: 15874059526
Email: weideng(at)nuaa.edu.cn
Address: 29 Yudao Drive, Building A9, Qinhuai, Nanjing
Introduction
Dr. Wei Deng is currently an associate professor of the Institute of Frontier Science (IFS) at Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics (NUAA). Dr. Deng’s current research focuses on advanced water treatment and purification, involving solar evaporation, superwetting membrane, and photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants.
Education
Aug. 2019, Ph.D. in Mechanical Engineering, Texas A&M University
Aug. 2016, M.S. in Mechanical Engineering, New York State University at Stony Brook
Jun. 2014, B.S. in Measurement and Control Technology and Instruments, University of Science and Technology of China
Work Experience
Nov. 2021 - present, Associate Professor
Institute of Frontier Science
Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics
Sep. 2019 – Jul. 2021, Visiting Assistant Professor
Department of Mechanical Engineering
Texas A&M University
Selected Research Work
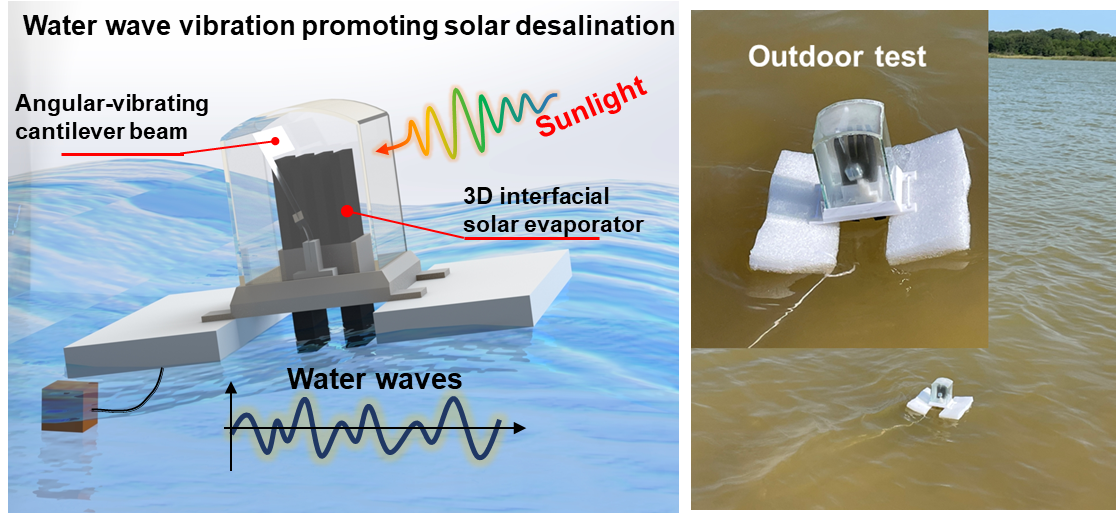
1. Water wave vibration-promoted solar evaporation
Interfacial solar evaporation holds great potential for water desalination. This work developed a novel system that had an interfacial solar evaporator integrated with an angularly vibrating cantilever beam, harnessing both solar and water wave energies when floating on water surfaces for efficient water desalination. Mechanism studies revealed that the vibrating cantilever beam promoted vapor flow and condensation on specific surfaces. This work provides new insights on advancing solar desalination with the simultaneous and rational utilization of multiple sustainable energy resources. (Nano Energy 92(2021): 106745)
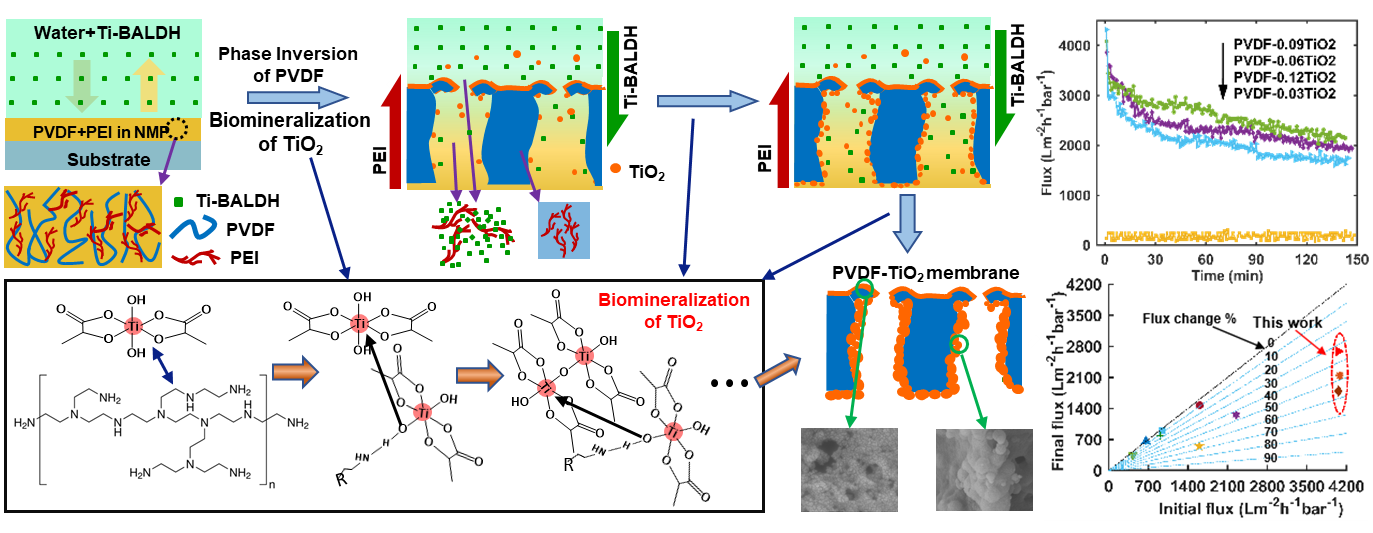
2. In situ biomineralization-constructed antifouling superwetting membranes
Antifouling capability is essential for superwetting nanocomposite membranes when treating oily wastewater. This work developed a novel in situ biomineralization method to fabricate superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic inorganic-organic nanocomposite membranes. Superior separation and antifouling performance were achieved when treating surfactant-stabilized oil in water emulsions. (Journal of Membrane Science 622 (2021): 119030)
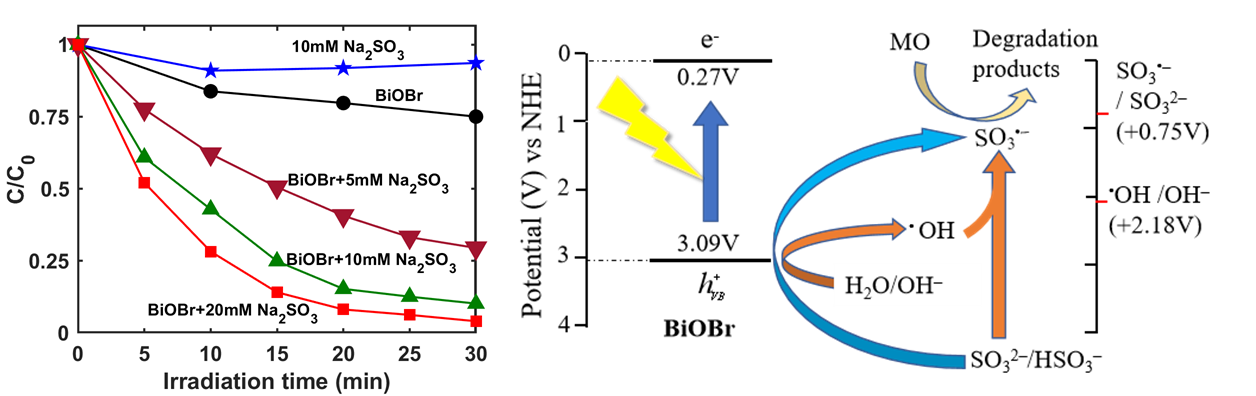
3. Sulfite-promoted photocatalytic degradation of organic water pollutants
Photocatalytic nanomaterials illuminated by sunlight are capable of degrading organic pollutants in wastewater through generating powerful radicals. This work for the first time discovered the unique contribution of sulfite to enhancing photodegradation efficiency. It was found that sulfite radicals were produced, via the reactions between sulfite anions and photo-induced holes/hydroxyl radicals, and degraded organic pollutants efficiently. (Environmental Science & Technology. 51.22 (2017): 13372-13379)
Research interests
Solar evaporation, antifouling superwetting membranes, photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants, nonlinear vibrational energy harvesting
Selected publications
1. Deng, W., Fan, T., Li, Y., Water Wave Vibration-Promoted Solar Evaporation with Super High Productivity. Nano Energy 92(2021): 106745.
2. Deng, W., Fan, T., Li, Y., In situ biomineralization-constructed superhydrophilic and underwater superoleophobic PVDF-TiO2 membranes for superior antifouling separation of oil-in-water emulsions. Journal of Membrane Science, 622 (2021): 119030.
3. Deng, W., Li, Y., Novel superhydrophilic antifouling PVDF-BiOCl nanocomposite membranes fabricated via a modified blending-phase inversion method. Separation and Purification Technology, 254 (2021): 117656.
4. Deng, W., Li, C., Pan, F., Li, Y., Efficient Oil/Water Separation by A Durable Underwater Superoleophobic Mesh Membrane with TiO2 Coating Via Biomineralization. Separation and Purification Technology, 222 (2019), 35-44.
5. Deng, W., Pan, F., Batchelor, B., Jung, B., Zhang, P., Abdel-Wahab, A., Zhou, H., Li, Y., Mesoporous TiO2–BiOBr microspheres with tailorable adsorption capacities for photodegradation of organic water pollutants: probing adsorption–photocatalysis synergy by combining experiments and kinetic modeling. Environmental Science: Water Research & Technology, 5 (2019), 769-781.
6. Deng, W., Zhao, H., Pan, F., Feng, X., Jung, B., Abdel-Wahab, A., Batchelor, B., Li, Y., Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of organic water pollutants promoted by sulfite addition, Environmental Science & Technology, 51 (2017) 13372-13379.
7. Deng, W., Wang, Y., A dual resonant rectilinear-to-rotary oscillation converter for low frequency broadband electromagnetic energy harvesting, Smart Materials and Structures, 26 (2017) 095059.
8. Deng, W., Wang, Y., Non-contact magnetically coupled rectilinear-rotary oscillations to exploit low-frequency broadband energy harvesting with frequency up-conversion, Applied Physics Letters, 109 (2016) 133903.
9. Deng, W., Wang, Y., Systematic parameter study of a nonlinear electromagnetic energy harvester with matched magnetic orientation: Numerical simulation and experimental investigation, Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 85 (2016) 591-600.
10. Deng, W., Wang, Y., Input-dependent performance study of a nonlinear piezoelectric energy harvester, Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 28 (2016) 619-626.