Science China Materials ,2022
Abstract:
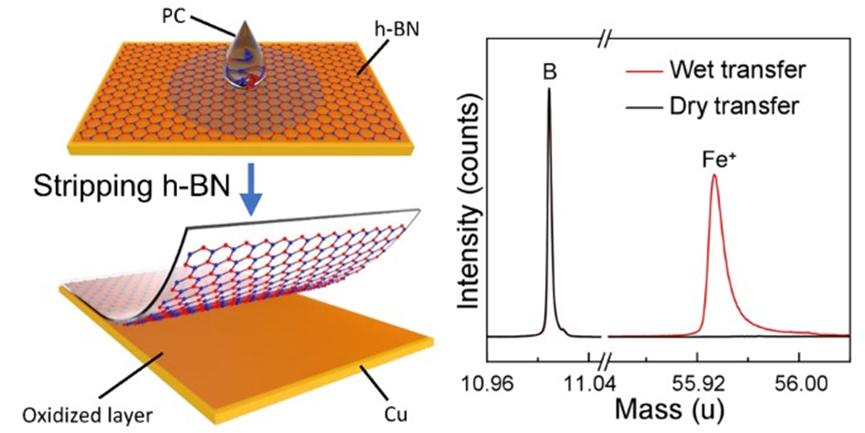
Hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) is an outstanding two-dimensional material in terms of thermal stability and chemical inertness, enabling its versatile applications under harsh conditions. However, the oxidation resistance of h-BN is significantly reduced in the presence of metallic catalysts, which could be readily introduced during commonly adapted transfer methods of chemical vapor-deposited samples through the wet etching of metallic substrates. Here we propose a clean dry transfer method for monolayer h- BN film grown on the copper (Cu) surface. Thus, the mechanical delamination of the h-BN film from the substrates becomes feasible as their interfacial adhesion energy is significantly reduced because of the oxygen intercalation and surface oxidation of Cu during exposure to air. The drytransferred h-BN film is proven to be free of metallic (iron) contaminants, in sharp contrast to the wet-transferred h-BN film, which contains significant amounts of metallic residues. The clean transfer of h-BN considerably enhances its oxidation resistance by 50–100°C, yielding nearly the ideal performance of h-BN. As a result, graphene layers coated with drytransferred monolayer h-BN film exhibit enhanced robustness to temperatures in the air up to 700°C, indicating the advantage of the proposed dry transfer method.
Link: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s40843-022-2112-y