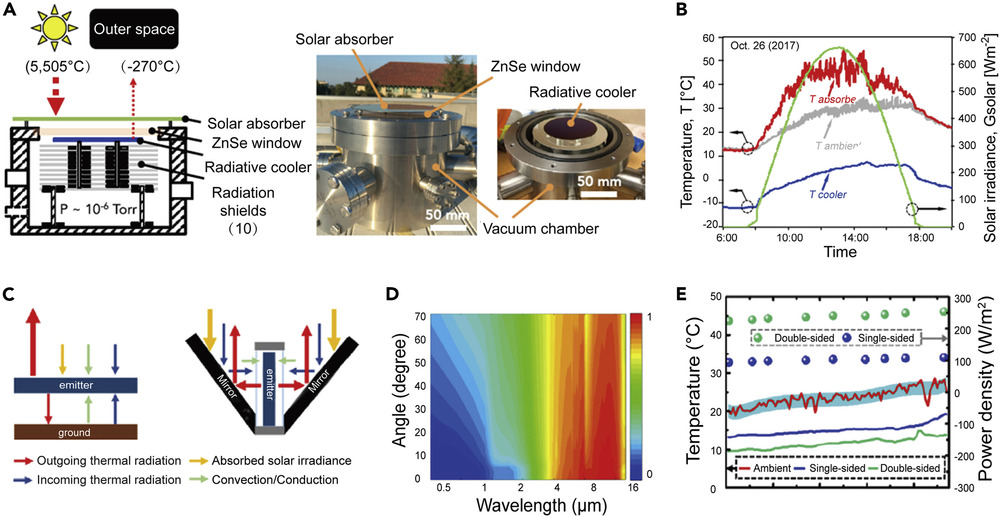
In recent years, sustainable energy development has become a major theme of research. The combination of solar heating and daytime radiative cooling has the potential to build a competitive strategy to alleviate current environmental and energy problems. Several studies on the combination of daytime radiative cooling and solar heating have been reported to improve energy utilization effificiency. However, most integrations still have a low solar/mid-infrared spectrum regulation range, low heating/cooling performance, and poor stability. To promote this technology further for real-world applications, herein we summarize the latest progress, technical features, bottlenecks, and future opportunities for the current integration of daytime radiative cooling and solar heating through the switch mode (including electrical, thermal-responsive, and mechanical regulations) and collaborative mode.