Jie Tan, Yufeng Guo*, Wanlin Guo.
Abstract:
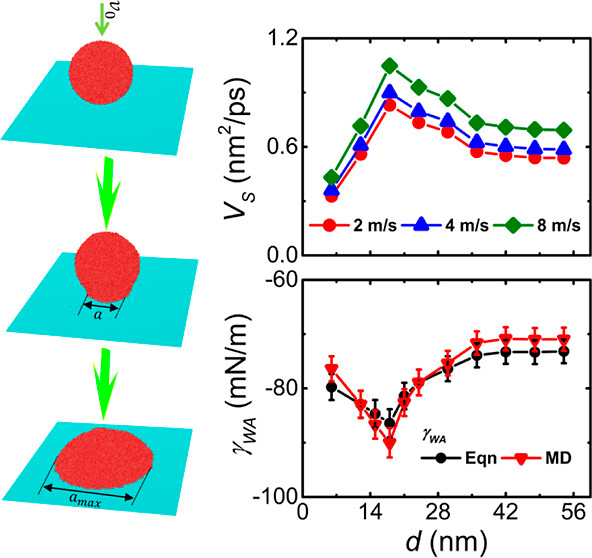
The impinging of water nanodroplets on solid surfaces is crucial to many nanotechnologies. Through large-scale molecular dynamics simulations, the size effect on the spreading of water nanodroplets after impinging on hydrophilic, graphite, and hydrophobic surfaces under low impinging velocities has been systematically studied. The spreading rates of nanodroplets first increase and then decrease and gradually become constant with the increase of nanodroplet diameter. The nanodroplets with the diameters of 17–19 nm possess the highest spreading rates because of the combined effect of the strongest interfacial interaction and the strongest surface interaction within water molecules. The highest water molecule densities, hydrogen bond numbers, and dielectric constants of interface and surface layers mainly contribute to the lowest interface work of adhesion and surface tension values at optimal diameters. These results unveil the nonmonotonic characteristics of spreading velocity, interface work of adhesion and surface tension with nanodroplet diameter for nanodroplets on solid surfaces.
Link:https://pubs.acs.org/doi/full/10.1021/acs.langmuir.3c00983
--校内链接--
--校外链接--

微信公众号