Abstract:
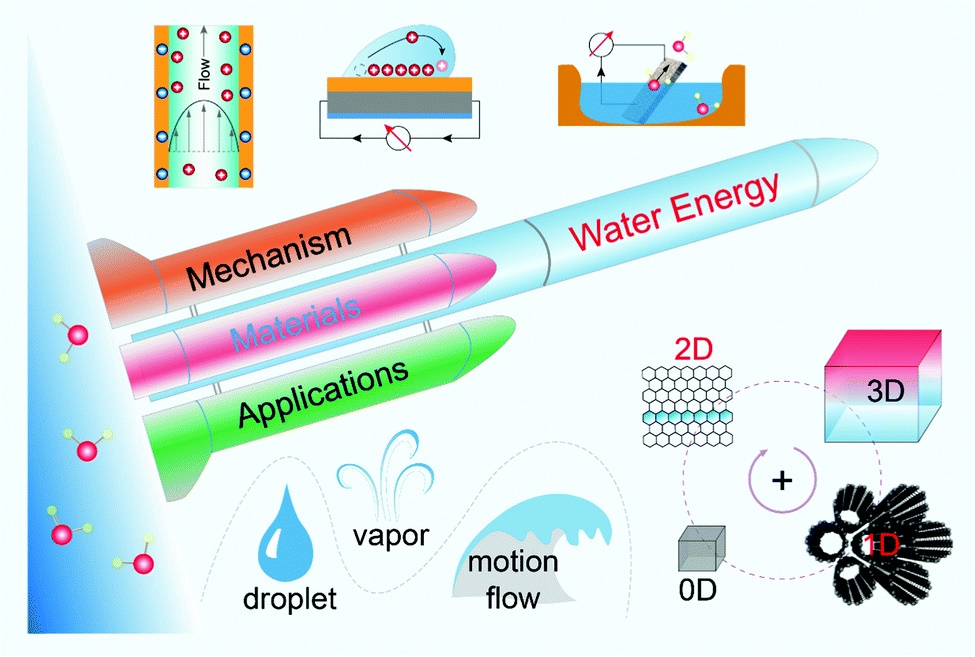
Water is a colossal reservoir of clean energy as it adsorbs thirty-five percent of solar energy reaching the Earth's surface. More than half of the adsorbed energy turns into latent heat for water evaporation, driving the water cycle of the Earth.1 Yet, only very limited energy in the water cycle is harvested by current industrial technologies. The past decade has witnessed the emergence of hydrovoltaic technology, which generates electricity from nanomaterials by direct interaction with water and enables energy harvesting from the water cycle such as from rain, waves, flows, moisture and natural evaporation. Years of efforts have been committed to improve the conversion efficiency of hydrovoltaic devices through chemical synthesis of advanced nanomaterials and innovative design of device structures. Further development of this field, however, still requires in-depth understanding of hydrovoltaic mechanisms and boosting of the electrical outputs for wider applications. Here, we present a tutorial review of different mechanisms of generating electricity from droplets, flows, natural evaporation and ambient moisture by analyzing basic interactions at various water–material interfaces. Key aspects in raising the output power of hydrovoltaic devices are then discussed in terms of material synthesis, structural design, and device optimization. We also provide an outlook on the potential applications of this technology ranging from sensors, power suppliers to multifunctional systems as well as on the scientific and technological challenges in transforming its potential into practical utility. The prospects of this emerging field are considered for future endeavor.
Link: https://doi.org/10.1039/D1CS00778E
--校内链接--
--校外链接--

微信公众号