Maolin Yu, Zhiqiang Zhao, Wanlin Guo, Zhuhua Zhang
Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,Volume 186, May 2024, 105579
Abstract
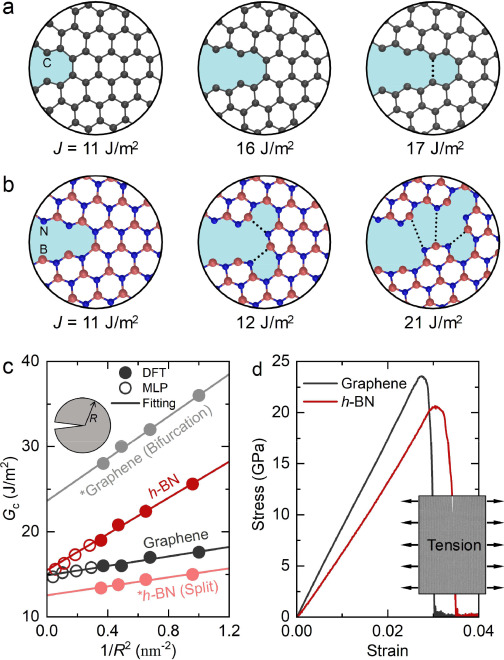
Two-dimensional materials (2DMs) are prone to brittle failure under load but a recent experiment has demonstrated intrinsic toughening in hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN), which calls for a general understanding of fracture toughness in 2DMs. Using atomistic calculations combined with a developed size-dependent extrapolation method, we show that 2DMs with strong anisotropy of edge energy favor bifurcated cracks for intrinsic toughening as in h-BN, while those with weak edge energy anisotropy exhibit split cracks for brittle failure as in graphene. The interplay between chemical bond strength and fracture energy of bifurcated crack tips leads to alternate deflections and, thus, rough crack edges as observed in the previous experiment. We further develop a robust descriptor for identifying 2DMs exhibiting similar fracture behavior to that in h-BN. More interestingly, we reach a physically interpretable formula capable of quantitatively determining the toughness of 2DMs based on easily accessible intrinsic features of elements. These findings lay a solid foundation for nanodevice applications where controlled toughness is required.
--校内链接--
--校外链接--

微信公众号