Xiao Wang , Zepu Kou , Yanshuang He , Xuemei Li , Xiaofei Liu , Jun Yin * , Wanlin Guo
Appl. Surf. Sci(IF:6.3),Available online 12 April 2025
ABSTRACT
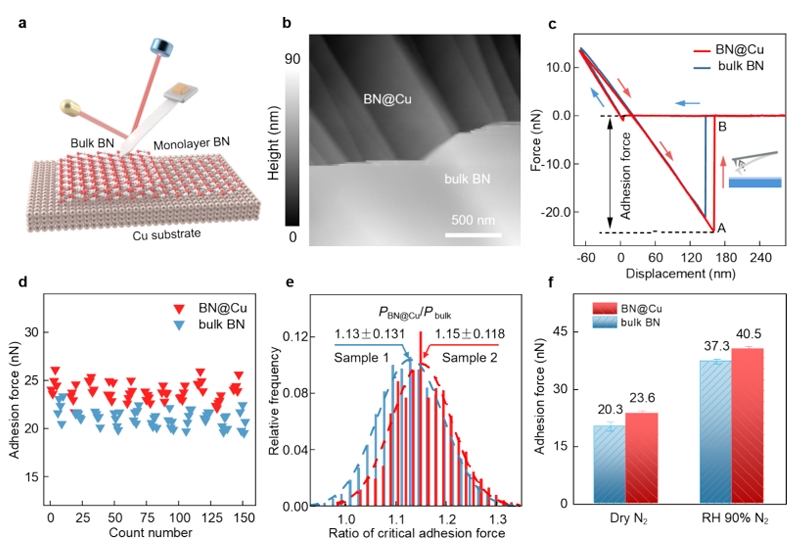
Interfacial van der Waals interactions are ubiquitous and play pivotal roles in diverse fields, ranging from microelectromechanical systems to atomic manufacturing. Clarifying its penetration depth and sub-surface contributions is crucial for revealing the structure–property relationship and its potential on-demand design. Taking inert monolayer boron nitride as a model system, we demonstrated that substrate notably contribute to its van der Waals adhesion with objects in contact with it. Atomic force microscopy spectrum and density functional theory calculations consistently indicate that the critical adhesion pressure exerted on the tip by copper- supported monolayer BN is stronger than that by bulk BN. Decoupling BN from copper through oxygen inter calation results in a notable reduction in surface adhesion. These results shed light on ways to modulating interfacial van der Waals interactions.
DOI:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2025.163261
--校内链接--
--校外链接--

微信公众号